All oral health articles
230 results




Bad Breath (Halitosis)
Treat Halitosis: 5 Quick Fixes to Cure Bad Breath
Bad breath is a common problem that can affect your everyday life. Click here to discover 5 quick fixes to cure bad breath.
Read More

Bad Breath (Halitosis)
Bad Breath From Dry Mouth And How To Treat It
Some people suffer with bad breath from dry mouth problems, which have little to do with poor hygiene. The good news is, you can take steps to identify and treat the problem, as well as prevent it from recurring.
Read More
Bad Breath (Halitosis)
The Best Mouthwash for Bad Breath: Key Ingredients to Look For
Mouthwashes fall into one of two categories: therapeutic or cosmetic. Cosmetic mouthwashes are those that mask bad breath, rather than get rid of the cause.
Read More
Bad Breath (Halitosis)
Morning Breath: Prevention, Treatment & Tips
The phone alarm sounds each morning waking you from a restful night's slumber. You rub the sleep from your eyes and then you notice it: morning breath.
Read More
Bad Breath (Halitosis)
Bad Breath From Stomach Problems? What It Means And How To Fix It
In fact, bad breath from stomach issues can be even more perplexing than typical bad breath, because it's harder to identify, isolate and treat. Learn more about what's causing your bad breath here.
Read More
Bad Breath (Halitosis)
How To Tell If You Have Bad Breath
Knowing how to tell if you have bad breath can be tricky, because you can't identify it yourself. Nonetheless, there are a few things you can do to improve it if needed.
Read More
Bad Breath (Halitosis)
How To Cure Bad Breath
Halitosis, more commonly known as bad breath, is an embarrassing hygiene issue that nobody wants to have. Read more at Colgate.com
Read More











Oral Care: Adults (18+)
Can Tooth Enamel Be Restored?
Can weakened tooth enamel be repaired? It depends on the state it's in. Keeping tooth enamel healthy is most effective when done through prevention. Here's how.
Read More
Oral Care: Adults (18+)
Bumps on the Back of the Tongue: Normal or Abnormal?
Bumps on the back of the tongue can occur due to sores and infections among other conditions. Consult your dentist if you notice abnormal bumps.
Read More
Oral Care: Adults (18+)
Choosing The Best Toothbrush For You
The best toothbrush for the job depends on a variety of things that are unique to you. Here are three things to look for in a product that does this.
Read More


Bridges & Crowns
Your Dental Crown Procedure: What To Expect
Your dentist may recommend that you undergo a dental crown procedure for one of several reasons:… Read more at Colgate.com
Read More










Adult Orthodontics
What Are The Different Types Of Braces, and Which Is Right for Me?
Your orthodontist may recommend any of the following types of braces or dental appliances to help correct your particular problem.
Read More





Cavities
What Is A Gumline Cavity?
Did you know that cavities can form in the pits & grooves of the molars, between teeth, or even along the gumline? Learn more about gumline cavities here.
Read More
Cavities
What Does Sugar Do To Teeth?
Sugar can lead to damage to teeth. Here's how you can prevent tooth decay from hijacking your family's oral health.
Read More


Dental Emergencies & Sports Safety
Dry Socket Symptoms: When, Where and Why Dry Sockets Happen
Read More

Dental Emergencies & Sports Safety
Four Options For Fixing A Chipped Tooth
Fixing a chipped tooth as soon as it happens ensures your mishap doesn't cause further problems, but what are your options? Find out more, here.
Read More

Dental Visits
How Often Should You Go To The Dentist?
While it’s true that a twice-yearly cleaning schedule is a good rule of thumb for many people, scheduling dentist appointments should be based on each person’s oral hygiene, habits and medical conditions.
Read More
Dental Visits
Dentist Requirements: What It Takes To Become A Dentist
Dentist requirements extend beyond additional education, though. Your dentist needed to pass a number of tests and more. Find out additional information here.
Read More









Dry Mouth
10 Home Remedies For Dry Mouth
Dry mouth can develop for many reasons: medication, nutritional deficiencies, stress, cancer treatment, and even some systemic diseases. Learn how to help dry mouth here.
Read More


Early Orthodontics
How Much Do Braces Cost?
So how much do braces cost for kids? First, it's necessary to identify the type of braces for your child and the duration of the treatment.
Read More






Fluoride
Can Fluoride Help Adults?
The use of fluoride can benefit both children and adults. Research has shown that fluoride applied directly to the teeth is important for fighting decay. Learn more here.
Read More
Fluoride
What Is Stannous Fluoride Toothpaste?
Stannous fluoride toothpaste is an oral care product that offers powerful benefits when used as part of a good oral hygiene routine. Here's what you need to know about its unique properties.
Read More
Fluoride
What Does Fluoride Do To Protect Your Smile?
If you've ever wondered what fluoride does to improve your oral health and fight cavities, here's what you need to know.
Read More
Fluoride
Should You Use a Fluoride Mouth Rinse?
As an adult, however, there are times when you are at higher risk for tooth decay, and a fluoride rinse may be an appropriate addition to your oral hygiene routine. Learn more here.
Read More
Fluoride
Why Use A Fluoride Free Toothpaste?
Should you be using a fluoride-free toothpaste? The answer has a lot to do with your age. Learn more about fluoride and whether to use it or not here.
Read More
Fluoride
Fluoride Dangers: How Much Is Too Much?
As the teeth develop, fluoride from water, food or supplements helps build strong tooth enamel, which is better able to resist decay. Learn more about fluoride here and how much is too much.
Read More
Fluoride
Fluoride for Babies: Is It Safe?
By sticking to some simple guidelines and portions, fluoride is safe and recommended for babies and young children. Find out what you need to know here.
Read More








Gum Disease (Gingivitis)
Four Questions You Might Have About Chlorhexidine Gluconate Mouthwash
Read More
Gum Disease (Gingivitis)
Bleeding Gums Treatment and Home Remedies
Bleeding gums when you brush or floss are often an early symptom of gum problems, which can lead to more advanced issues.
Read More
Gum Disease (Gingivitis)
How to Treat Gingivitis
Gingivitis can be reversed by eliminating the tartar and biofilm build-up that are causing the irritation in your gums. Learn more here.
Read More














Oral Care: Kids (5-12)
Toddler Tooth Decay and How to Prevent It
Toddler tooth decay is a concern for parents because nearly a quarter of under 5s develop a cavity in their primary teeth.
Read More
Oral Care: Kids (5-12)
Best Toothpaste For Kids With Cavities
For kids, tooth decay is a common problem. What is the best toothpaste for kids who have cavities? Find out at Colgate.com.
Read More



Mouth & Teeth Anatomy
How to Get Rid of a Dry Throat
Wondering how to get rid of a dry throat? Learn about some of the common causes, including allergies, dehydration, the common cold and more.
Read More




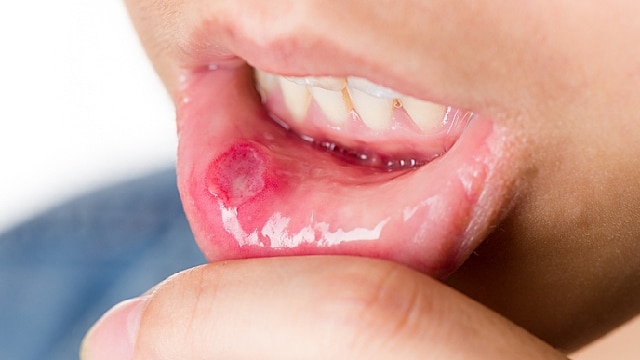




Mouth Sores and Infections
How to Get Rid of a Cold Sore Fast
These sores are common and will go away on their own, but if you have a major event coming up, you might be wondering how to get rid of a cold sore fast.
Read More
Mouth Sores and Infections
How to Prevent a Cold Sore Scab
If you suffer from cold sores, you know that the accompanying redness and blisters can make you feel self-conscious. But when those blisters become scabs and possibly scars, what should be a fairly short-term issue can have long-term repercussions. Cold sore scabs can be the result of picking and irritation, so make sure that you properly care for and prevent cold sores to stop them from becoming worse over time. By educating yourself on what can cause a cold sore scab and result in scarring, you can heal faster so cold sores don't become a permanent problem.
Read More


Mouth Sores and Infections
Managing A Blood Blister In The Mouth
If you've ever had the displeasure of accidentally biting your cheek while chewing food, you might recall a sore forming in the area. While mouth sores caused by cheek biting are usually no cause for concern, what if you notice a sore in the mouth that's filled with blood? Finding a blood blister in the mouth may be worrying, but rest assured that these blisters are generally harmless and may heal on their own.
Read More


























Plaque & Tartar
Tartar Deposits on Teeth: Treatment and Prevention
Tartar build-up on teeth can often be prevented by regular brushing, but you'll need the help of your dentist to remove it if it decides to stick around.
Read More



Dental Product Guidance
Choosing The Best Toothbrush For You
The best toothbrush for the job depends on a variety of things that are unique to you. Here are three things to look for in a product that does this.
Read More

Dental Product Guidance
How Does Mouthwash Work? Answering your mouthwash questions
What type of mouthwash should you choose? How does mouthwash work? This guide will answer those questions and more.
Read More

Dental Product Guidance
What Products Are Available From My Dentist For Home Tooth Whitening?
Read More







Teeth Whitening
Best Whitening Toothpaste: Five Signs You've Picked A Winner For A Perfect Smile
Read More




Teeth Whitening
Is Teeth Whitening Safe?
Many people wish their teeth were whiter, but are nervous about bleaching treatment. So, is teeth whitening safe? Yes, save three common side effects.
Read More
Teeth Whitening
Teeth Whitening: Which method is best for you?
Many people want a whiter smile, so how do you choose the best teeth whitening system for you? Find out more about teeth whitening systems here.
Read More
Teeth Whitening
Is the Cost of Professional Teeth Whitening Worth It?
If you've considered whitening your teeth, you may already know the professional teeth whitening cost can be high — much more expensive than at-home alternatives. Learn more here.
Read More
Teeth Whitening
5 Common Teeth Whitening Mistakes
For the best results, check with your dentist before bleaching and avoid some of the following teeth whitening mistakes.
Read More
Teeth Whitening
What are the best Instant Teeth Whitening Options?
Here are your options, including the fastest teeth whitening treatments, and the ones that take some time.
Read More




Jaw Pain (TMD)
Three Ways A TMJ Massage Can Relieve Jaw Pain
A TMJ disorder is usually the result of inflamed and painful chewing muscles around your jaw. Luckily, a TMJ massage can act as an effective, non-medicinal solution.
Read More

Tooth Fairy
How to Write a Letter From the Tooth Fairy
A tooth fairy letter can help children answer questions about their teeth as well as encourage kids to take care of their teeth. Find out more, here.
Read More



Tooth Extraction
Dry Socket Prevention: Caring For Yourself After An Extraction
A tooth extraction should be uneventful, and if you follow a few dry socket prevention tips, your recovery will be just as smooth. Find out more, here.
Read More
Tooth Extraction
Pain After Having a Tooth Removed: 3 Tips to Help Your Kids Keep Brushing
Read More










Tooth Sensitivity
How Tooth Nerve Pain Occurs
Here are some foods and drinks to avoid when suffering from tooth pain, and some insight into how the nerve becomes exposed in the first place.
Read More
Tooth Sensitivity
Preventing and Treating Exposed Dentine
Exposed dentine can be annoying and painful, but there are many ways to prevent enamel erosion and treat the related tooth sensitivity. Find out more, with Colgate®.
Read More

Tooth Sensitivity
Treat Super-Sensitive Teeth With Sensitive Toothpaste
Sensitivity in the teeth can be uncomfortable and inconvenient. Fortunately, sensitive toothpaste can often be the answer to your pain by Colgate.
Read More


Tooth Sensitivity
What Causes Tooth Sensitivity & How to Treat It
It is estimated that one in eight people in the United Kingdom experience tooth sensitivity. So what causes sensitive teeth? Any number of dental problems. Find your answers here.
Read More





Veneers
All About Veneers: How Long They Last and How To Care For Them
How long do veneers last? The answer depends heavily upon how you care for them. Learn how to care for them and more, here.
Read More









Wisdom Teeth
What Age Do Wisdom Teeth Come In?
If you and your teen are maintaining your regular dental appointments, you'll be in good stead to track that the wisdom teeth are erupting healthily or catch if they need intervention.
Read More
Wisdom Teeth
Wisdom Teeth Symptoms That Indicate It's Time For Extraction
Have you ever felt like you were teething as an adult? It was probably in the back of your mouth, and the swelling you felt there was really a tooth trying to erupt.
Read More




