Dentures are replacements for missing teeth that can be taken out and put back into your mouth. While dentures take some getting used to, and will never feel exactly the same as one's natural teeth, today's dentures are natural looking and more comfortable than ever.
There are two main types of dentures: full and partial. Your dentist will help you choose the type of denture that's best for you based on whether some or all of your teeth are going to be replaced and the cost involved.
How do Dentures Work?
With full dentures, a flesh-colored acrylic base fits over your gums. The base of the upper denture covers the palate (the roof of your mouth), while that of the lower denture is shaped like a horseshoe to accommodate your tongue.
Dentures are custom-made in a dental laboratory from impressions taken of your mouth. Your dentist will determine which of the three types of dentures described below is best for you.
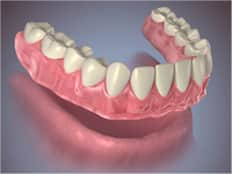
Conventional or Immediate Full Denture.
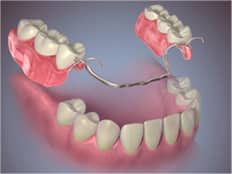
Partial Denture.
- Conventional Full Denture
A conventional full denture is placed in your mouth after any remaining teeth are removed and tissues have healed. Healing may take several months, during which time you are without teeth.
- Immediate Full Denture
An immediate full denture is inserted immediately after the remaining teeth are removed. (Your dentist takes measurements and makes models of your jaw during a prior visit.) While immediate dentures offer the benefit of never having to be without your teeth, they must be relined several months after being inserted. The reason is that the bone supporting the teeth reshapes as it heals, causing the denture to become loose.
- Partial Denture
A partial denture rests on a metal framework that attaches to your natural teeth. Sometimes crowns are placed on some of your natural teeth and serve as anchors for the denture. Partial dentures offer a removable alternative to bridges.
How Long Before I Get Used to My Dentures?
New dentures may feel awkward or uncomfortable for the first few weeks or even months. Eating and speaking with dentures might take a little practice. A bulky or loose feeling is not uncommon, while the muscles of your cheeks and tongue learn to hold your dentures in place. Excessive saliva flow, a feeling that the tongue does not have adequate room, and minor irritation or soreness are also not unusual. If you experience irritation, see your dentist.
How Long do Dentures Last?
Over a period of time, your denture will need to be relined, remade, or rebased due to normal wear. Rebasing means making a new base while keeping the existing denture teeth. Also, as you age, your mouth naturally changes. These changes cause your dentures to loosen, making chewing difficult and irritating your gums. At a minimum, you should see your dentist annually for a checkup.
Here are tips for caring for your dentures:
- When handling your dentures, stand over a folded towel or basin of water. Dentures are delicate and may break if dropped.
- Don't let your dentures dry out. Place them in a denture cleanser soaking solution or in plain water when you're not wearing them. Never use hot water, which can cause them to warp.
- Brushing your dentures daily will remove food deposits and plaque, and help prevent them from becoming stained. An ultrasonic cleaner may be used to care for your dentures, but it does not replace a thorough daily brushing.
- Brush your gums, tongue and palate every morning with a soft-bristled brush before you insert your dentures. This stimulates circulation in your tissues and helps remove plaque.
See your dentist if your dentures break, chip, crack or become loose. Don't be tempted to adjust them yourself-this can damage them beyond repair.